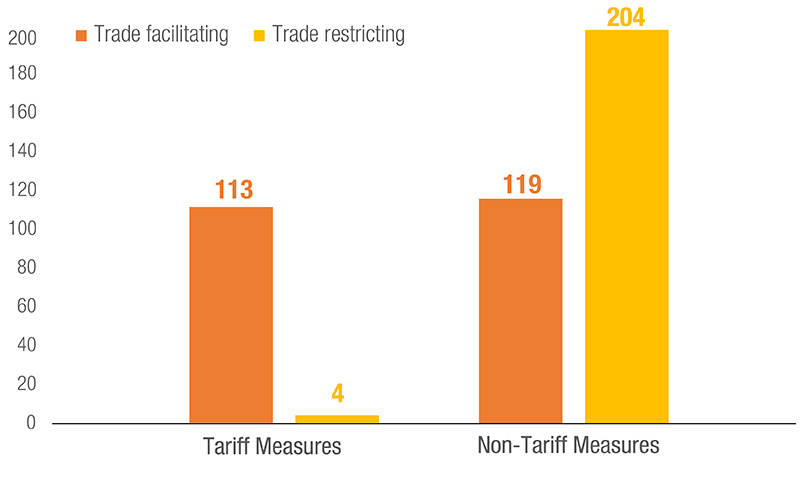
Governments across the world used several trade policy instruments to respond to the various challenges and pressures created by the COVID-19 pandemic. Both tariff and non-tariff measures were applied: some sought to facilitate trade, and others restricted it.
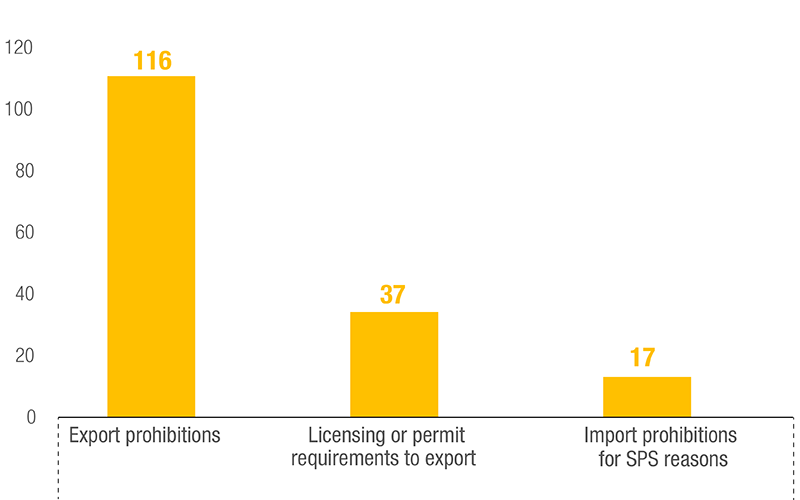
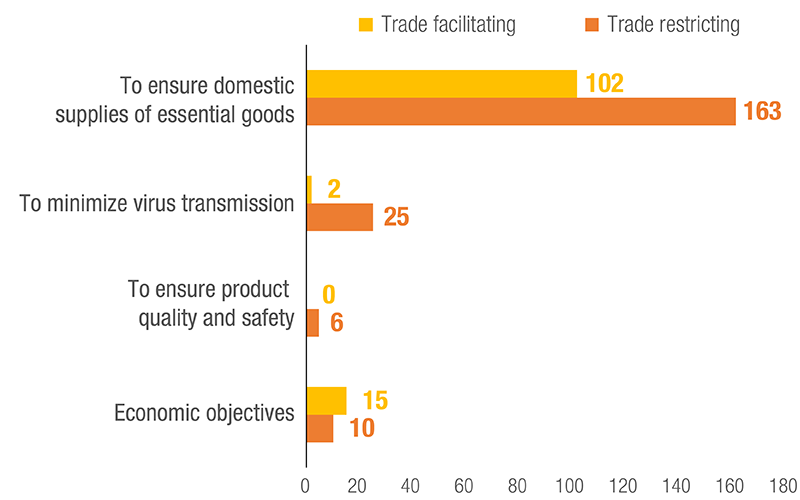
The use of NTMs was noticeable with 323 measures applied, as of 31 August 2021. Trade restricting NTMs included export restrictions of various forms to prevent shortages of essential goods, and stricter SPS requirements to ensure product quality and safety.
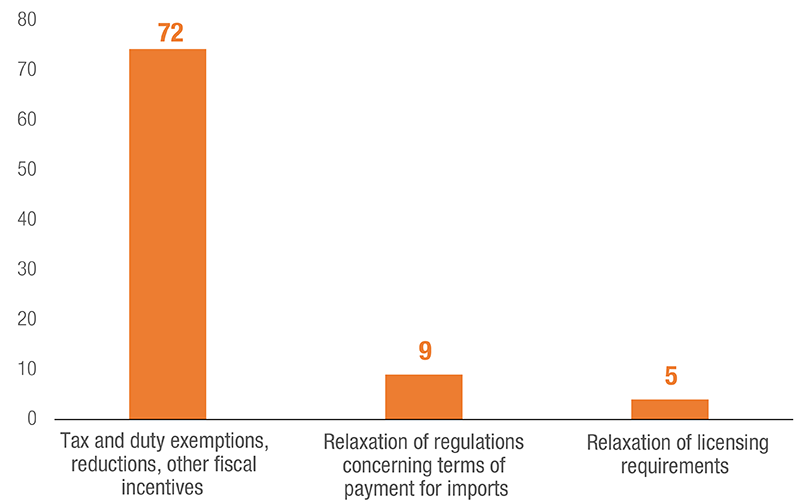
Measures to facilitate trade involved relaxation of authorization and licensing requirements as well as exemption from various forms of taxes on imported products.
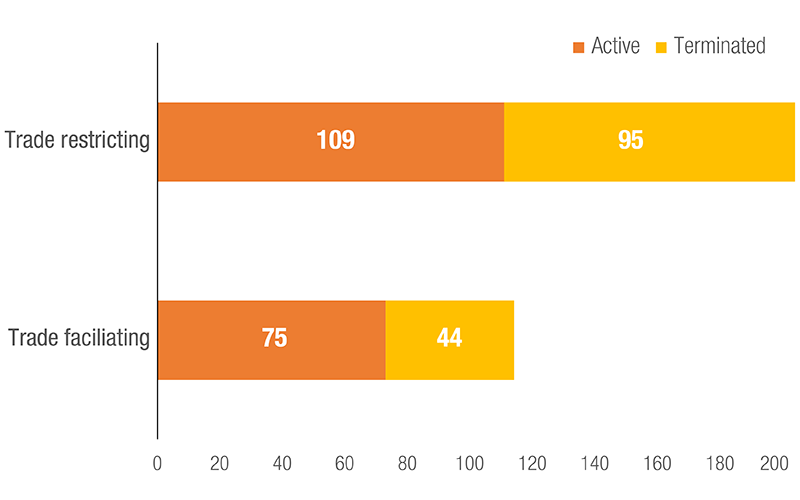
Medical goods, essential food products and some non-essential items were subject to trade measures. UNCTAD estimates that approximately 43% of all trade restrictive NTMs have been terminated, as of 31 August 2021. However, 57% of them are still in place and NTMs on vaccines appeared.
COVID-19 trade measures
Quick Facts (August 2021)
COVID-19 Trade Measures
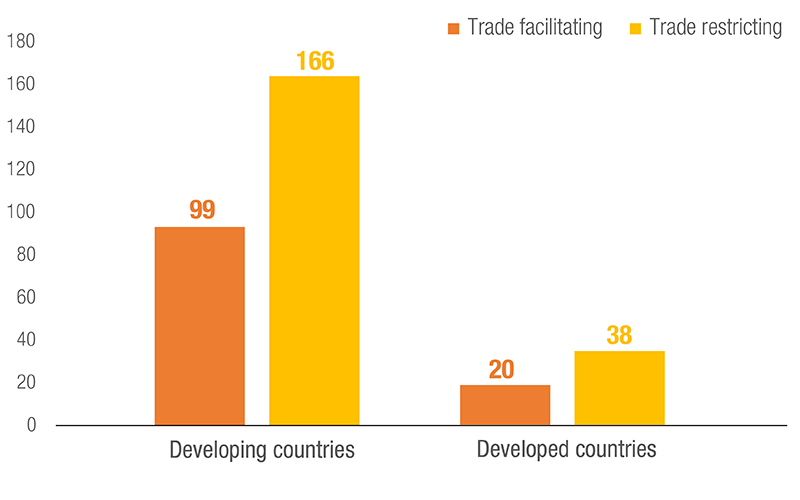
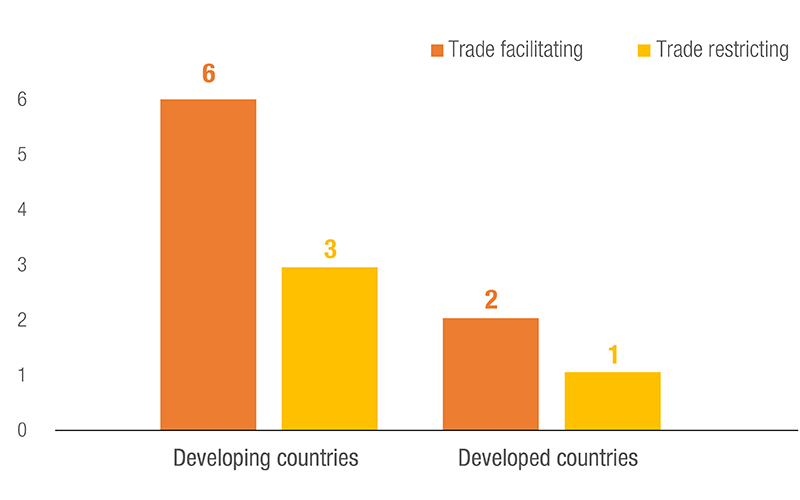
Number of NTMs used, by Development Status
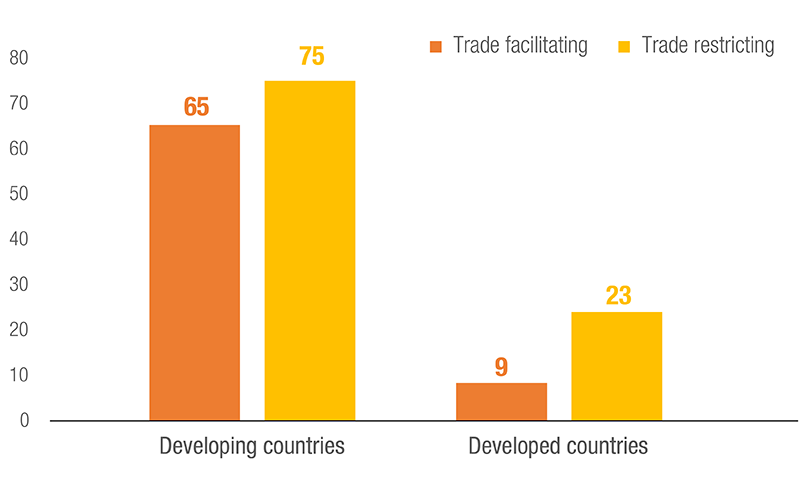
Number of Countries/Customs Territories using NTMs
Frequently used Trade Restricting NTMs
Frequently used Trade Facilitating NTMs
NTMs classification: Chapter-wise Breakdown
NTMs: Objectives
NTMs: Status
NTMs: Timeline
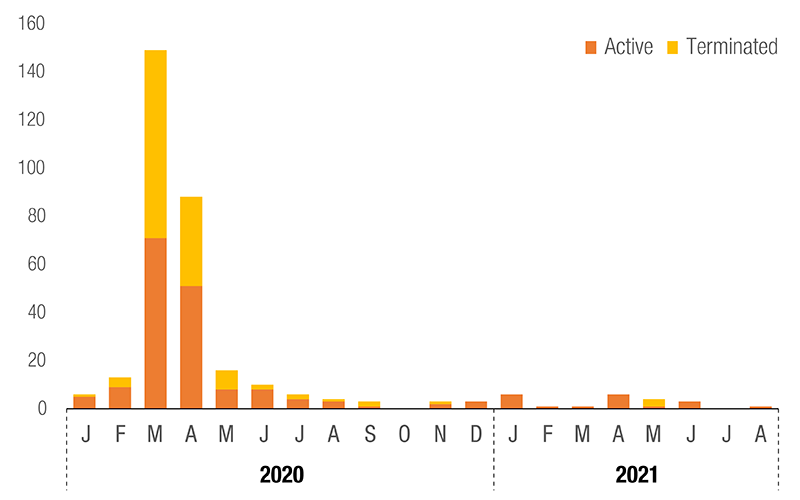
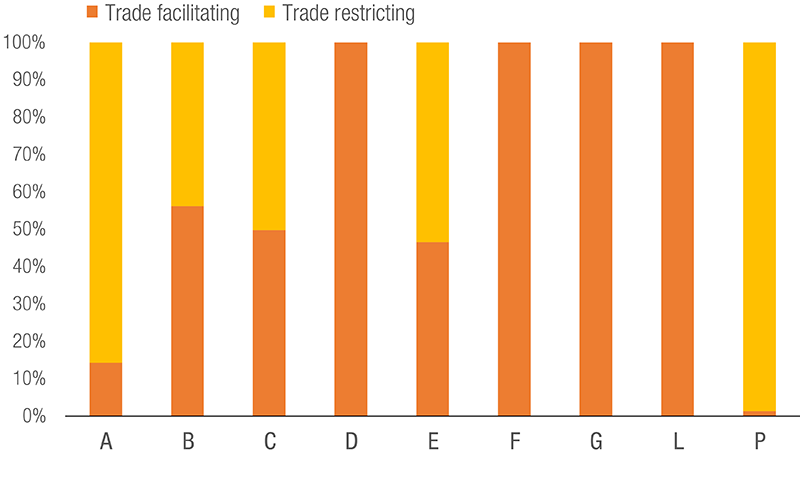
NTMs: Product Coverage
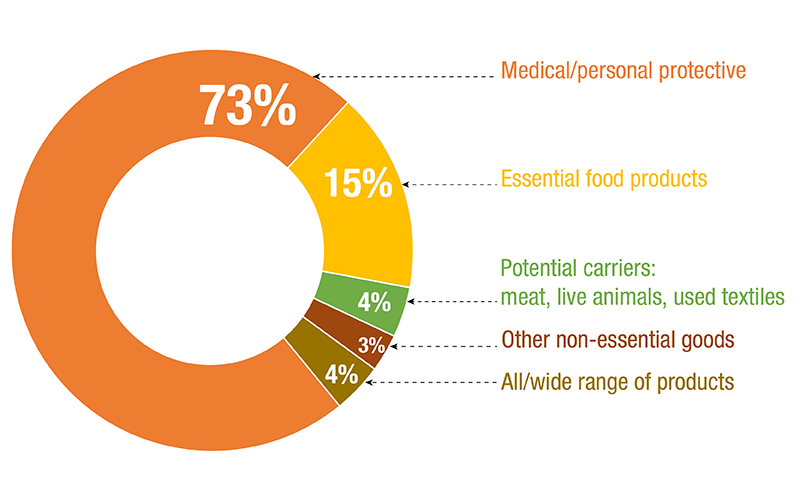
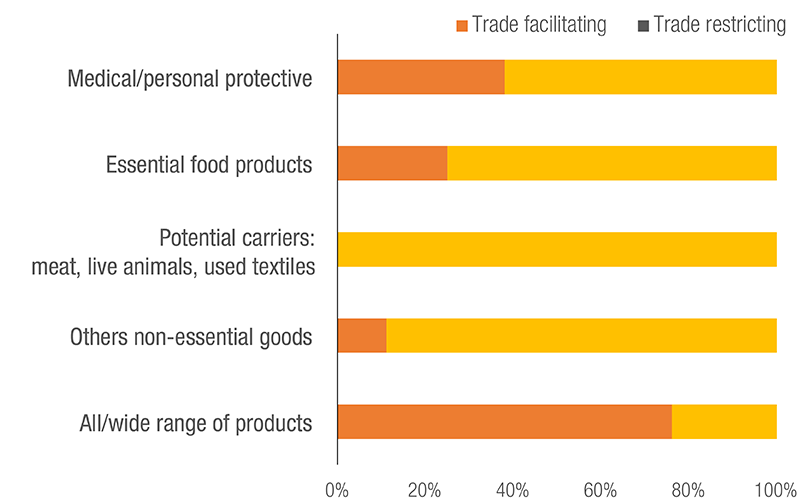
Status of NTMs, by Product Type
NTMs on COVID-19 Vaccines
Methodology
The UNCTAD COVID-19 NTM dataset builds on databases - WTO COVID-19: Measures affecting trade in goods; WTO Quantitative restrictions; Global Trade Alert and ITC COVID-19 Temporary Trade Measures, with additional UNCTAD research covering national government websites of laws and regulations as well as news media sources. Noting that many COVID-19 NTMs go through a cycle of establishment stage, gradual phase-out stages and termination stage, UNCTAD structured the dataset in which one measure represents one whole cycle, rather than an individual stage. Then, UNCTAD categorized the type of NTMs by using the International Classification of NTMs and added additional variables such as product category and development status of imposing country.
Commonly used NTMs
|
Trade Facilitating Measures |
Trade Restricting Measures |
|---|---|
|
L41* Tax and duty exemptions, reductions, other fiscal incentives reducing burden of taxes otherwise due |
P31 Export prohibition |
|
G4 Regulations concerning terms of payment for imports |
P33 Licensing, permit or registration requirements to export |
|
E125* Licensing for the protection of public health |
A11 Prohibitions for SPS (sanitary and phytosanitary) reasons |
|
A83* Certification requirements for SPS (sanitary and phytosanitary) reasons |
E313 Temporary prohibition, including suspension of issuance of licenses |
|
L11 Transfers of funds (monetary transfers) by the Government (to an enterprise) – Grants |
P32 Export quotas |
|
D12* Anti-dumping duties |
P22 Export monitoring and surveillance requirements |
|
B83* Certification requirements for TBT (technical barriers to trade) reasons |
E325 Prohibition for the protection of public health |
|
L9 Support for consumers or producers not elsewhere specified |
C9 Other pre-shipment inspection formalities not elsewhere specified |
|
E325 Prohibition for the protection of public health |
B14 Authorization requirements for importing certain products TBT (technical barriers to trade) reasons |
|
B7* Product quality, safety, or performance requirements for TBT (technical barriers to trade) reasons |
|
|
B14* Authorization requirements for importing certain products TBT (technical barriers to trade) reasons |
|
* Measures relaxed to facilitate trade
Implications for Trade
Many measures such as exemptions from duties and taxes (L41); relaxation of SPS requirements (A83, B7, B14 and B83) and easing of non-automatic licensing requirements (E125) on imported medical supplies helped expedite trade of such goods, thus ensuring adequate supplies for the source country.
On the other hand, use of export prohibitions (P31); export quotas (P32); licensing, permit or registration requirements to export (P33) on medical supplies negatively affected trade and hence the availability of essential goods in import-dependent countries, particularly the most vulnerable ones. These measures, often imposed without coordination with trading partners disrupted global value chains, further impeding smooth flow of trade in critical goods.
Some measures like export monitoring and surveillance requirements (P22) helped ensure that the exported product was safe and of high quality. However, they also ended up delaying exports due to the additional inspections and checks imposed.



 Download:
Download:



