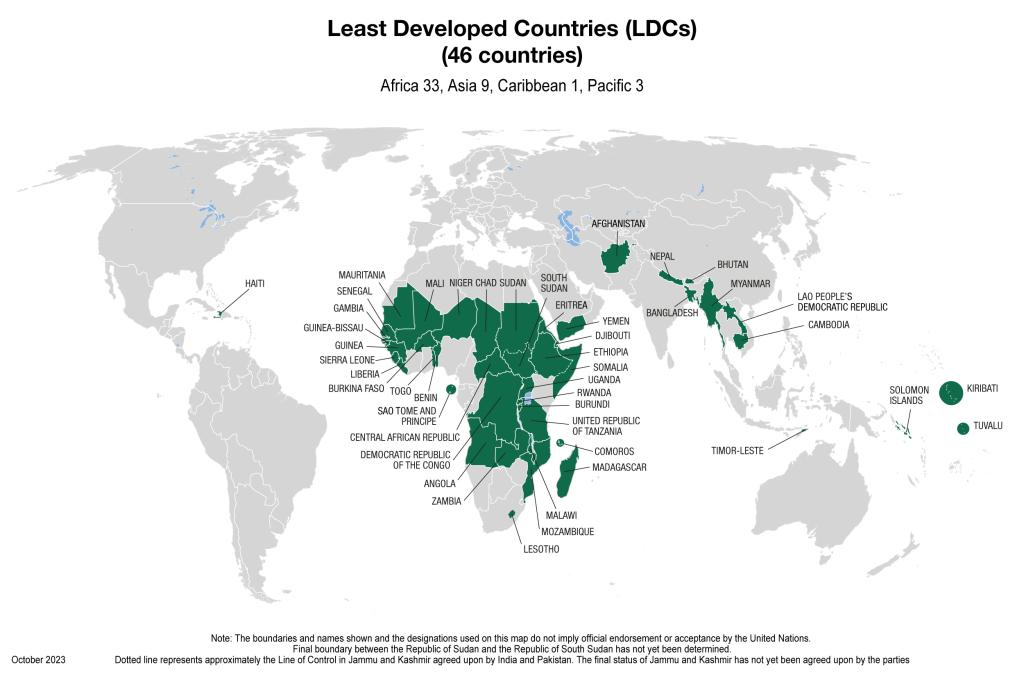
There are currently 46 economies designated by the United Nations as the least developed countries (LDCs), entitling them to preferential market access, aid, special technical assistance, and capacity-building on technology among other concessions. These 46 LDCs are distributed among the following regions:
- Africa (33): Angola, Benin, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Central African Republic, Chad, Comoros, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Djibouti, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Gambia, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Lesotho, Liberia, Madagascar, Malawi, Mali, Mauritania, Mozambique, Niger, Rwanda, Sao Tome and Principe, Senegal, Sierra Leone, Somalia, South Sudan, Sudan, Togo, Uganda, United Republic of Tanzania and Zambia
- Asia (9): Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Cambodia, Lao People’s Democratic Republic, Myanmar, Nepal, Timor-Leste and Yemen
- Caribbean (1): Haiti
- Pacific (3): Kiribati, Solomon Islands and Tuvalu
Establishment of the list of the least developed countries
The list of LDCs is reviewed every three years by the Committee for Development Policy (CDP), a group of independent experts that report to the Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) of the United Nations. Following a triennial review of the list, the CDP may recommend, in its report to ECOSOC, countries for addition to the list or graduation from LDC status.
The next triennial review is scheduled to take place in March 2024. The CDP is bound to apply the criteria and the thresholds for inclusion into the LDC category and for graduation from the category as follows:
- An income criterion, based on a three-year average estimate of the gross national income (GNI) per capita in United States dollars. The threshold for inclusion is $1,088 or below; the threshold for graduation is $1,306 or above.
- A human assets index (HAI), consisting of two sub-indices: a health sub-index and an education sub-index. The health sub-index has three indicators: (i) the under-five mortality rate; (ii) the maternal mortality ratio; and (iii) the prevalence of stunting. The education sub-index has three indicators: (i) lower secondary school completion rate; (ii) adult literacy rate; and (iii) gender parity index for lower secondary school completion. All six indicators are converted into indices using established methodologies with an equal weight. The thresholds for inclusion and graduation are 60 or below and 66 or above, respectively.
- An economic and environmental vulnerability index (EVI), consisting of two sub-indices: an economic vulnerability sub-index and an environmental vulnerability sub-index. The economic vulnerability sub-index has four indicators: (i) share of agriculture, forestry and fishing in GDP; (ii) remoteness and landlockedness; (iii) merchandise export concentration; and (iv) instability of exports of goods and services. The environmental vulnerability sub-index has four indicators: (i) share of population in low elevated coastal zones; (ii) share of the population living in drylands; (iii) instability of agricultural production; and (iv) victims of disasters. All eight indicators are converted into indices using established methodologies with an equal The thresholds for inclusion and graduation are 36 or above and 32 or below, respectively.
At each triennial review, all countries in developing regions are reviewed against the criteria. If a non-LDC meets the established inclusion thresholds for all three criteria in a single review, it can become eligible for inclusion. Inclusion requires the consent of the country concerned and becomes effective immediately after the General Assembly takes note of the Committee’s recommendation. No recommendations were made for inclusion at the CDP’s 2021 triennial review.
To graduate from the LDC category, a country must meet the established graduation thresholds of at least two of the criteria for two consecutive triennial reviews. Countries that are highly vulnerable, or have very low human assets, are eligible for graduation only if they meet the other two criteria by a sufficiently high margin. As an exception, a country whose per capita income is sustainably above the “income-only” graduation threshold, set at three times the graduation threshold ($3,918), becomes eligible for graduation, even if it fails to meet the other two criteria.
LDC graduation
Six countries have graduated from least developed country status:
- Botswana in December 1994;
- Cabo Verde in December 2007;
- Maldives in January 2011;
- Samoa in January 2014;
- Equatorial Guinea in June 2017; and
- Vanuatu in December 2020.
The CDP has recommended graduation from the LDC category for several countries in the past. Among them, Bhutan is scheduled for graduation on 13 December 2023. Angola, Sao Tome and Principe and Solomon Islands are slated for graduation in 2024.
The CDP’s 2021 Triennial review recommended for graduation from the LDC category Bangladesh, Lao People’s Democratic Republic and Nepal. Because of the COVID-19 pandemic, the Committee recommended an extended preparatory period of five years, as well as careful monitoring and analysis of the impacts of the pandemic, and specific transition support. This recommendation was endorsed by ECOSOC resolution 2021/11, issued on 8 June 2021, and by the General Assembly resolution 76/8, issued on 24 November 2021.
In the CDP’s 2021 review of the list of LDCs, the following countries were found to have met the graduation thresholds for the first time: Cambodia, Comoros, Djibouti, Senegal and Zambia. Djibouti met the "income-only" criterion; Comoros, Senegal and Zambia met the graduation thresholds for two of the three criteria, namely income and human assets; and Cambodia met all three graduation criteria (income, human assets, and economic and environmental vulnerability). These countries will be reviewed again in 2024 and, if they meet the criteria for a second time, could be recommended for graduation.
Kiribati and Tuvalu were recommended for graduation in 2018 and 2012 respectively but ECOSOC deferred a decision on their graduation in 2018. In 2021 the CDP reiterated its recommendation of graduation but proposed a preparatory period of five years for these two countries. In resolution 2021/11, ECOSOC, recalling its decision to defer the consideration of the graduation of Kiribati and Tuvalu to no later than 2021, recognized the unprecedented socioeconomic impacts of the COVID-19 global pandemic, and decided to defer the consideration of their graduation until 2024.
The Committee decided to defer its decision on the cases of Myanmar and Timor-Leste to the CDP’s 2024 Triennial review.
For more information, please see the full Least Developed Countries Report 2023.
-------------------------
About UNCTAD
UNCTAD is the UN’s leading institution dealing with trade and development. It is a permanent intergovernmental body established by the United Nations General Assembly in 1964.
UNCTAD is part of the UN Secretariat and has a membership of 195 countries, one of the largest in the UN system. UNCTAD supports developing countries to access the benefits of a globalized economy more fairly and effectively.
We provide economic and trade analysis, facilitate consensus-building, and offer technical assistance to help developing countries use trade, investment, finance and technology for inclusive and sustainable development.
-------------------------



